Source : https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/strategy-data
Context and Objectives
With the rise of digital technologies, the volume of data generated has exploded, affecting all sectors of the economy and society. The EU recognizes the potential of this data to foster innovation, improve public services, and stimulate economic growth. The European Data Strategy aims to:
- Create common European data spaces where information can flow freely across sectors and countries, to create a genuine single market.
- Ensure that the rules for accessing and using data are fair, practical, and clear, with appropriate governance mechanisms.
- Ensure the availability of high-quality data to support creation and innovation.
Pillars of the Strategy
The strategy is based on four main pillars: 1
- A Data Governance Framework: In the process of establishing clear rules for data access and use, including through legislative measures such as the Data Governance Act and the Data Act.
- Infrastructures and Technologies: Invest in federated cloud infrastructures and common European data spaces to facilitate secure data sharing and storage.
- Skills: Strengthen digital skills and data literacy, focusing on SMEs and individuals, to ensure effective data use.
- Common European Data Spaces: Develop dedicated spaces in key sectors such as health, industry, agriculture, finance, energy, tourism (like DEPLOYTOUR!), and public administrations to encourage data sharing and usage.
Data Spaces: An Innovative Model for Data Sharing
A Data Space is defined as “an ecosystem where independent entities share data securely and sovereignly, relying on common standards, models, and architectures to ensure interoperability and trust”. 2
They aim to ensure interoperability, trust, and data protection while fostering innovation and competitiveness.
In the tourism sector, we find the Austrian Tourism Data Space, while EONA-X also focuses on tourism, with an added emphasis on mobility and transport. In the cultural sector, the Europeana Cultural Data Space is another example. All of these projects are included in DEPLOYTOUR.
In the European context, several initiatives play a crucial role in structuring and supporting the development of Data Spaces. The Data Space Support Center (DSSC), for example, serves as a key enabler, providing expertise and guidance to organizations looking to create or participate in Data Spaces, ensuring that they adhere to the necessary frameworks and standards. Similarly, the International Data Spaces Association (IDSA) fosters the creation of secure and trusted data exchange environments across sectors by providing technical standards and reference architectures to ensure data sovereignty and privacy. 3 4
The GAIA-X initiative is another cornerstone of the European data ecosystem, aiming to establish a federated data infrastructure for Europe. GAIA-X seeks to ensure that data exchanges within Europe are secure, transparent, and under European values, with a focus on creating a decentralized data infrastructure that promotes innovation while safeguarding data privacy. 5
Additionally, Simpl is an important initiative aimed at streamlining the process of data sharing across different industries and sectors in the EU. By simplifying the exchange protocols, it ensures that data sharing can occur efficiently while maintaining high standards for security and compliance with European regulations. 6
These initiatives work together to create an integrated and interoperable data landscape in Europe, facilitating the secure and sovereign sharing of data across industries and sectors, and fostering a data-driven economy that benefits all stakeholders.
Common European Data Spaces: A Structured Sectoral Approach
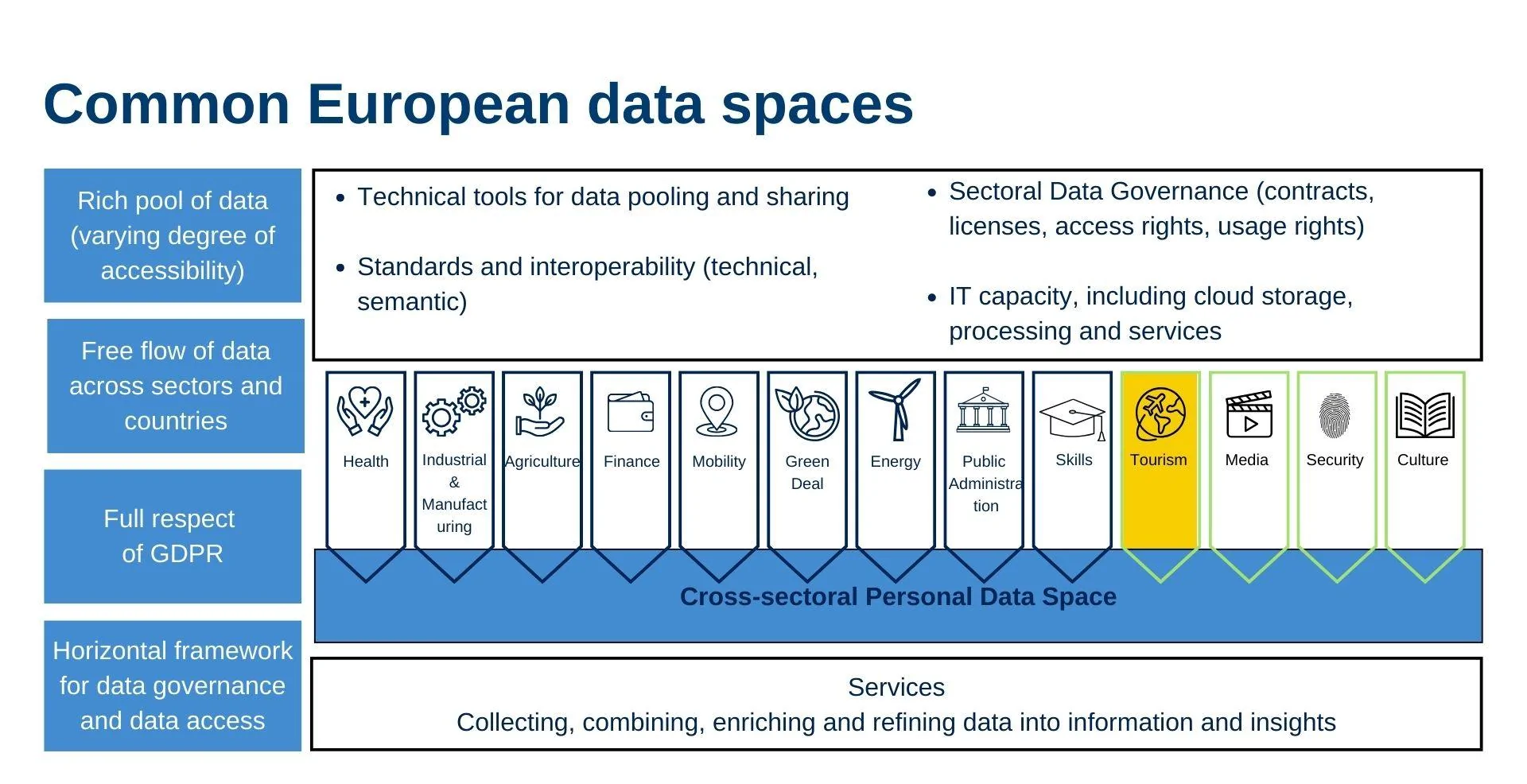
In this context, with the development of data spaces, the EU has launched a specific initiative: the Common European Data Spaces. Data spaces are secure environments for data sharing between organizations, whereas Common European Data Spaces are an EU initiative to create harmonized sectoral spaces to foster data discovery across Europe. These sectoral spaces aim to foster data sharing in strategic areas with a harmonized regulatory framework and suitable infrastructures.
The Common European Data Spaces include sectors such as tourism. In this context, the European project DEPLOYTOUR, aims to deploy a Common European Data Space for Tourism, to boost the competitiveness, sustainability, and resilience of the tourism sector.
Its main objectives are:
- Improve access to tourism data by reducing fragmentation and inaccessibility
- Build an operational federation of data spaces with a common governance
- Support the digital and environmental Tourism’s Transition Pathway
- Empower SMEs and DMOs in their digital and green transition
- Create new business models supporting the EU data economy
Expected Impact of the European Data Strategy
The implementation of an ambitious European data strategy is expected to bring benefits at multiple levels: 7
- Strong Economic Impact: Here’s the reformulation in English:
- The European Commission estimates that the data economy could represent €829 billion in 2025, compared to €301 billion in 2018, and is expected to reach €1,000 billion by 2030, highlighting significant growth in this sector.
- Improved Public Services: Particularly in healthcare and transportation.
- Enhanced Digital Sovereignty: By reducing Europe’s dependency on global actors in critical industries.
The European Data Strategy is a key initiative for Europe’s digital future. It not only ensures fair and secure access to data but also creates a real engine for innovation. With initiatives such as Data Spaces and Common European Data Spaces, the EU aims to make data a lever for competitiveness and sovereignty in the decades to come.
Sources :
- 1 www.europarl.europa.eu
- 2 dssc.eu
- 3 DSSC (Data Spaces Support Centre): www.dssc.eu
- 4 IDSA (International Data Spaces Association): internationaldataspaces.org
- 5 Gaia-X: www.gaia-x.eu
- 6 Simpl: www.simpl-programme.ec.europa.eu
- 7 www.digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu
